Cardio B 60 Capsules
To purchase Cardio B 60 Capsules, please call 800-921-4271 for approval.
Once approved, you’ll be able to log in and access the full product details.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Shipping & Return
Shipping & Return
Shipping
Shipping and handling charges are a flat rate of $4.95 for all Standard Shipping method orders and FREE for orders over $75 within the contiguous U.S. only, excluding Hawaii, Alaska & Puerto Rico.
30 Day Hassle Free Returns
If you’re not satisfied with our product, simply contact us and we’ll give you a full, 100% hassle-free refund.
Description
Description
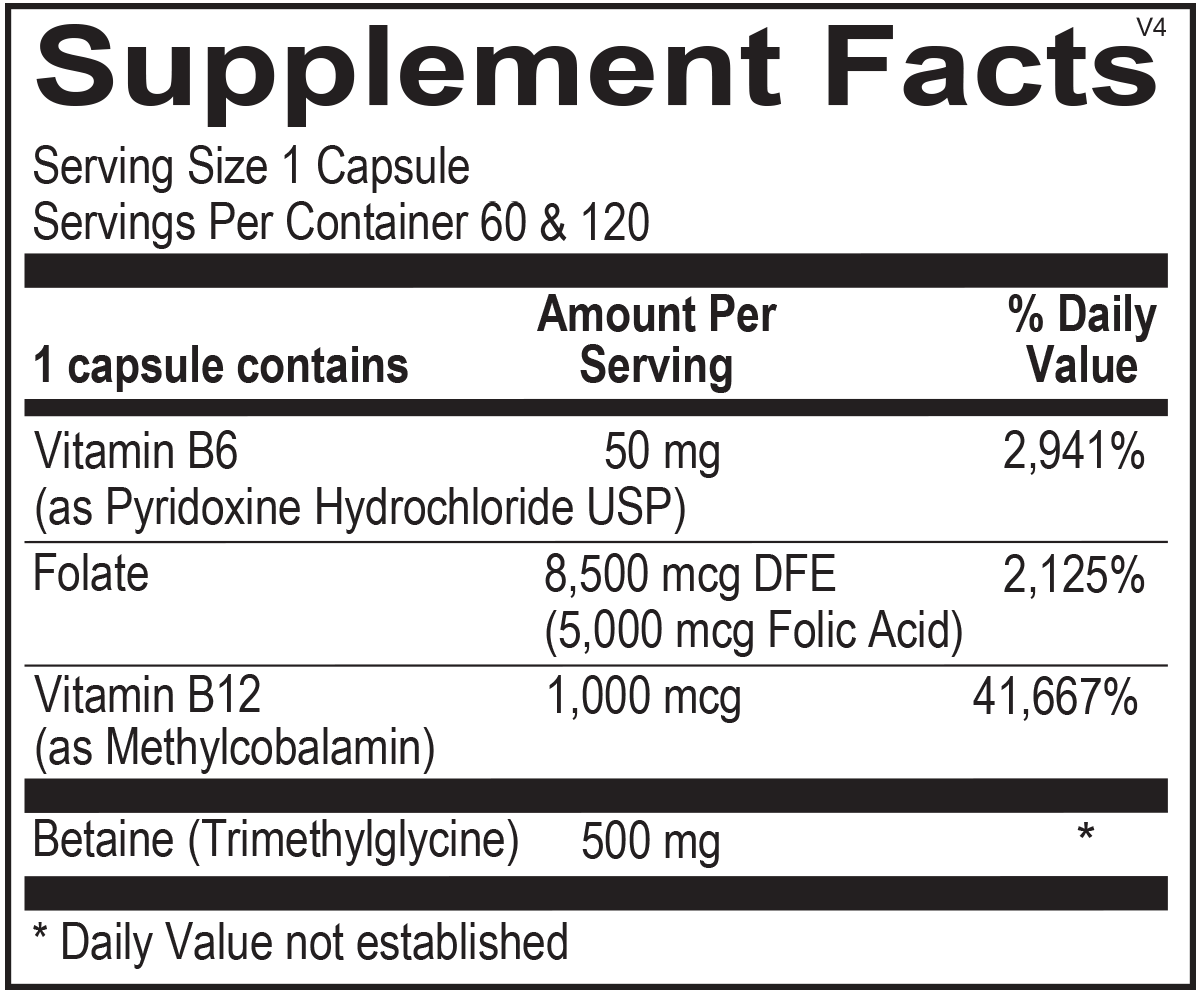
Cardio B uses higher doses of folic acid, B12, B6 and betaine (TMG), all in just one capsule a day, to aggressively support the primary pathways of maintaining homocysteine balance.
Why these natural ingredients?
Formula Synergy: Cardio B uses higher doses of folic acid, B12, B6 and betaine (TMG), all in just one capsule a day, to aggressively support the primary pathways of maintaining homocysteine balance.
Folic Acid: Folic acid is a B vitamin that increases red-blood-cell balance and helps break down and utilize protein. It is essential for DNA and RNA synthesis and thus is important for healthy cell division and replication. It is an essential nutrient for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, and folic acid supplementation can support healthy homocysteine levels. Cardio B has an aggressive 5mg-dose per capsule, giving your patients the intensive support they need to maintain normal homocysteine levels.
Vitamin B12: B12 is considered by many to be the second most important nutrient in balancing homocysteine levels. It is a required co-factor in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine via the folate pathway. Vitamin B12 shortfall is common in the elderly and those consuming vegetarian diets.
Vitamin B6: Another important ingredient for homocysteine metabolism, Vitamin B6 is known to maintain balanced homocysteine levels, even amongst those who have previously supplemented folic acid alone. Betaine (Trimethyl glycine) Betaine (TMG) acts as a strong methyl donor to homocysteine—converting it to methionine. This conversion pathway occurs in the liver and kidney and can contribute to enhanced homocysteine balance in those patients with impaired methionine metabolism.